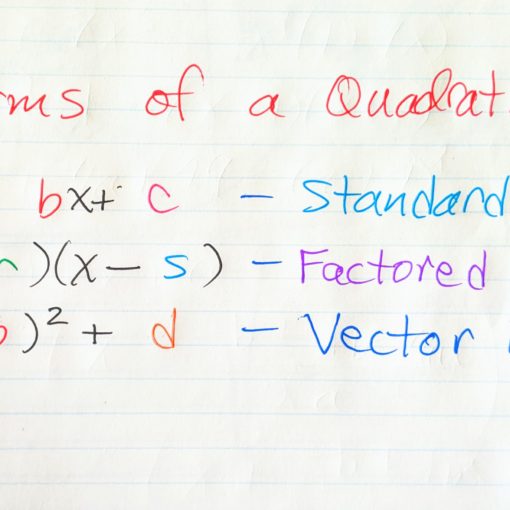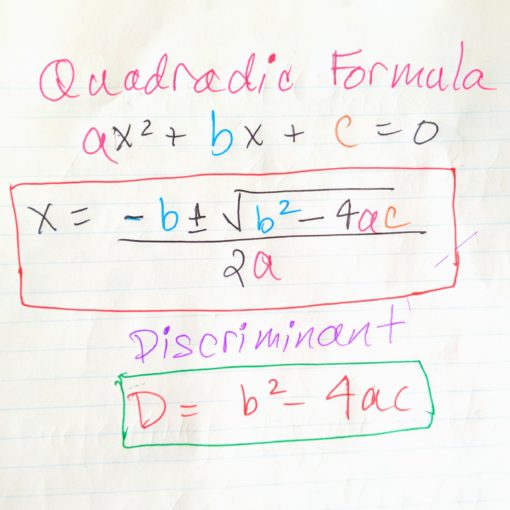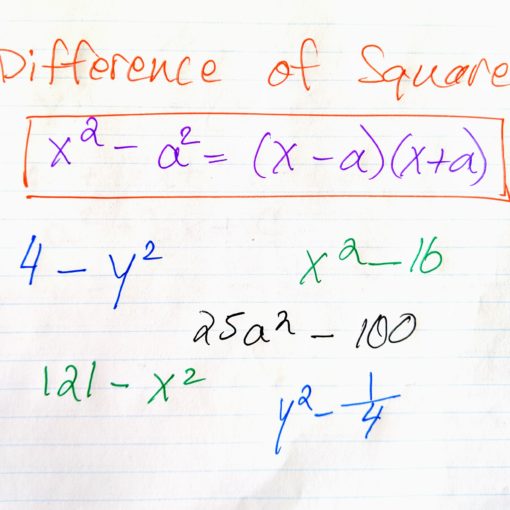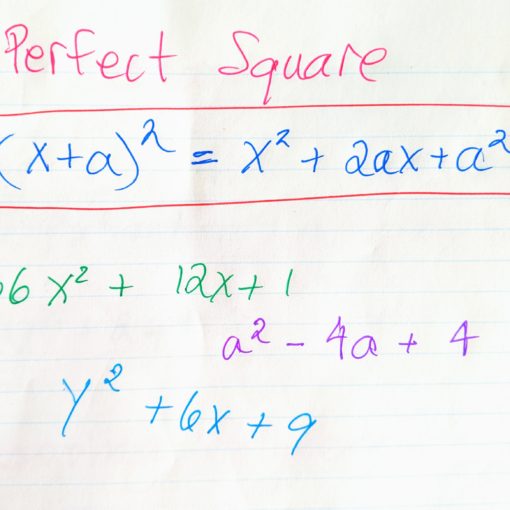Learn what x-intercepts and what y-intercepts of a function are. Learn how to locate the x and y intercepts of a function.
curriculum: Newfoundland
A quadratic is a polynomial of degree 2. There are different forms to represent this second degree polynomial: standard form, factored form and vector form. Depending on a particular problem, a different form will be more or less advantageous to use.
When we are faced with a quadratic that is not “nice” to factor we need to find a way to factor it. This is where the quadratic formula comes in. The discriminant is a value that can be calculated for each quadratic equation. Depending on the value of the discriminant, we can determine if the quadratic equation has a solution, or has factors, or not.
Quadratics are polynomials of degree 2. These polynomials have some interesting properties. There are quadratics with special structures such as perfect squares and differences of squares. Many quadratics can be factors and we will be looking at how to factor different quadratics. Here we are introducing you to quadratics and how to factor “nice” quadratics.
The difference of squares is another specially structured quadratic. A difference of squares has a very specific factorization which we will learn about.
A perfect square a quadratic with a specific structure. This structure allows for a very specific factorization. We will learn how to factor a perfect square and practice how to identify a perfect square.
You have seen factors of numbers and looked for common factors among pairs of numbers. Here we will look at polynomials and how to find the factors of a polynomial.